|
Low Power Quality Samples
>Low power quality is called the
deviation from the ideal voltage
waveform.
Short Term Changes
Voltage drop: The
nominal line voltage is between 1%
and 90% between 0.5 and 1 minute.
The general resources of the voltage
drop are the input of the large
asynchronous motor or the network
malfunctions (phase-to-ground-phase
faults).
Voltage Swell: gthe
opposite of the voltage drop. The
nominal line voltage is reduced from
110% to 180% from 0.5 cycles to 1
minute. General causes of failure;
line faults (voltage increase in
fault-free phase due to
phase-by-fault), switching of large
loads, switching of large capacitor
banks, faults in distribution
transformer exchangers. Voltage
peaks are characterized by magnitude
and occurrence times. The intensity
of the voltage rise is a function of
the fault location, system impedance
and grounding. In the case of a
phase-to-earth fault in a
non-grounded system, the
phase-to-earth voltage in the
non-earthed phase will be 1.73 times
the normal.
Interruption: This is less than 10%
of the voltage which does not last
longer than 60 seconds
KInterruption (Interruption): does
not last more than 60 seconds in
voltage.
Temporary Events
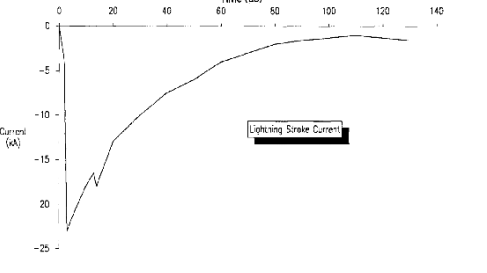
Impulsive transient: two-way abrupt
short changes in voltage or current.
They are characterized by rise and
fall times. For example, the sudden
transient change of 2000V to 1.2 /
50 microseconds increases to 1.2
microseconds and reaches a peak of
2000V, decreasing to half of its
peak in 50 microseconds. Causes,
lightning drops, inductive loads is
the introduction of. If the level of
these transient events is high, it
will cause the equipment to shut
down. By using temporary voltage
suppressors such as zener diode,
varistor, the effects can be
reduced. Because they are high
frequency, they can be easily
suppressed by resistive loads, do
not act much more than their source.
The temporal event characteristic of
a region within the building may be
very different. These distortions
can trigger resonant circuits in
power systems and may lead to
releasing regimes.
Sudden changes (Impulsive transient): Two-way
sudden short changes in voltage or
current. They are characterized by
rise and fall times. For example,
the sudden transient change of 2000V
to 1.2 / 50 microseconds increases
to 1.2 microseconds and reaches a
peak of 2000V, decreasing to half of
its peak in 50 microseconds. Causes,
lightning drops, inductive loads is
the introduction of. If the level of
these transient events is high, it
will cause the equipment to shut
down. By using temporary voltage
suppressors such as zener diode,
varistor, the effects can be
reduced. Because they are high
frequency, they can be easily
suppressed by resistive loads, do
not act much more than their source.
The temporal event characteristic of
a region within the building may be
very different. These distortions
can trigger resonant circuits in
power systems and may lead to
releasing regimes.
 |
|
Oscillatory transient changes:): two-way
sudden short changes in voltage or
current. They are classified as
high, low and medium frequency
variations according to their
frequencies. The oscillations
greater than 500 kHz are classified
as high-friction. These are the
changes that occurred after the
anisalinm. They are medium
frequencies between 5-500kHz. In
sequence capacitor switching,
medium-frequency oscillatory changes
are present in the current. 5khz is
called low frequency changes.
Voltage Fluctuations
Voltage fluctuations: less
than 5% of the line voltage. Loads
of continuous and rapid change in
current size, called flicker, cause
voltage fluctuations. The voltage
fluctuations are the reaction of the
three systems to the loads, and the
light flicker is the visible
reaction of the luminosity system in
human eyes.
Voltage Imbalance
Imbalance:: 3-phase voltage is
different from each other. Voltage
imbalance is the ratio of negative
or zero component to positive
component. Negative or zero stress
components result from unbalanced
loads causing unbalanced currents to
be drawn in power systems.r.
|

